Electric cars can be charged using a home charging unit or at public charging stations. The time it takes to charge an electric car depends on several factors, including the size of the battery, the charging method, and the charging speed. Generally, using a Level 1 charging outlet at home can take up to 20 hours to fully charge, while Level 2 charging stations can take 4-8 hours. DC fast charging stations can provide up to 80% charge in as little as 20-30 minutes.
To start electric mobility it is essential to a fast, reliable, and safe system of charging for the electric car. Electric mobility will never become reliable and comfortable until there are charging facilities in predictable ranges. The investment in charging infrastructure is a long-term business. Similar was the construction of the gasoline stations a century ago. Fast charging has a big role in the electric car industry. We have heard about AC and DC charging, below are some information.
Alternative Current Charging(AC)
The flow of energy on the electricity grid is of alternating current. All household appliances use this type of energy. Just to operate an electric car the battery needs direct current. So the current must be converted. To convert the current is necessary three main pieces.
The first part is the AC/DC converter. It converts the power from AC to DC. The second is the charging cable with a connector that is used to transfer the power from the external power source to the electric car through the vehicle inlet.
The third part is a charge controller responsible for the connection, protection, and control of the charging process. They control the charging current and ensure the optimal temperature between cells of the battery.
An example of a converter is the on-board charger. The size and weight of the onboard charger are dependent on the maximum charging power. Typically, the onboard charger has maximum power in the range of 1.9-22Kw. If the range power increase the onboard charger dimensions will also increase. However, the onboard charger dimensions are limited due to vehicle size.
Direct Current Charging(DC)
The solution to increasing the charging power is to move the AC/DC charger converter outside the vehicle. This is an off-board charging solution, it is named DC charging.
With no size and weight restrictions, the DC charger has a maximum charging power 50-350Kw. The DC power aliments directly the car.
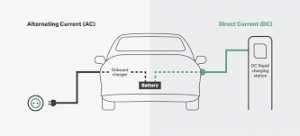
Of course in the care have both AD and DC charging which could use depending on the situation. Most vehicles have separate vehicle inlet for AC and DC charging.
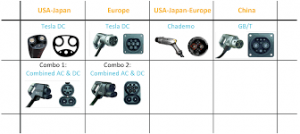
Types of Connectors
The connectors are divided according to the AC and DC charging by the connector type and charging power levels.
For AC charging- Type 1 connector is using in the USA and Japan, while Type 2 and 3 are using in Europe.
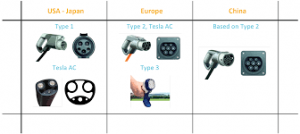
For DC charging- the CHAdeMO Type 4 connector is using by Japanese manufacturers globally, while the American and European car manufacturers are using a combined AC/DC connector CCS-COMBO. Tesla uses the same connector meant for AC charging for DC charging as well. China has its own DC connectors.
Charging Modes
There are three common methods of charging electric cars: Level 1, Level 2, and DC fast charging. Level 1 charging uses a standard household outlet (120 volts) and is the slowest charging option. Level 2 charging requires a special charging unit (240 volts) and is faster than Level 1. DC fast charging uses high-powered charging units (up to 600 volts) and can provide a significant charge in a short amount of time.
AC and DC charging power can be divided into three levels. Level 1 goes up to 10Kw power, Level 2 has a charging power up to 50Kw. Both AC and DC can provide Level 2 power. Over 50Kw, only DC charging is capable to provide charging power as high as 350Kw.
This level (Level 3) name it fast charging.
We can measure the range per hour of charging. Supposing that a car drives 5Km using 1 Kwh of energy.
Level1/AC and DC/0-10Kw power/ range of 50-250 per hour of charging
Level2/AC and DC/10-50Kw power/ range of 50-250 per hour of charging
Level3/Only DC/50-350Kw power/ range of 250-1750 per hour of charging
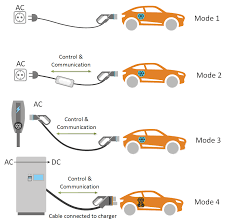
Mode1- This is the slow AC charging, there is no connection between the vehicle and the charging point.
Mode2- A slow AC charging from a regular electricity socket. In plus the charging cable has an In Cable Control and Protection Device (IC-CPD).
Mode3- This mode provides both slow and semi-fast charging through a charging station. The charging station is responsible for the control, communication, and protection of the charging process.
Mode4- This mode uses a specific socket for electric vehicles. Has a cable with a plug to use for DC charging. In the case of DC charging, the AC/DC connecter is located in the charging station.
electric car charging stations
Electric car charging stations are becoming more common, and are typically found at public locations such as parking lots, shopping centers, and rest areas. Some charging stations are free, while others require payment or a membership. Charging stations can be found using various mobile apps, online maps, or built-in navigation systems in electric cars.