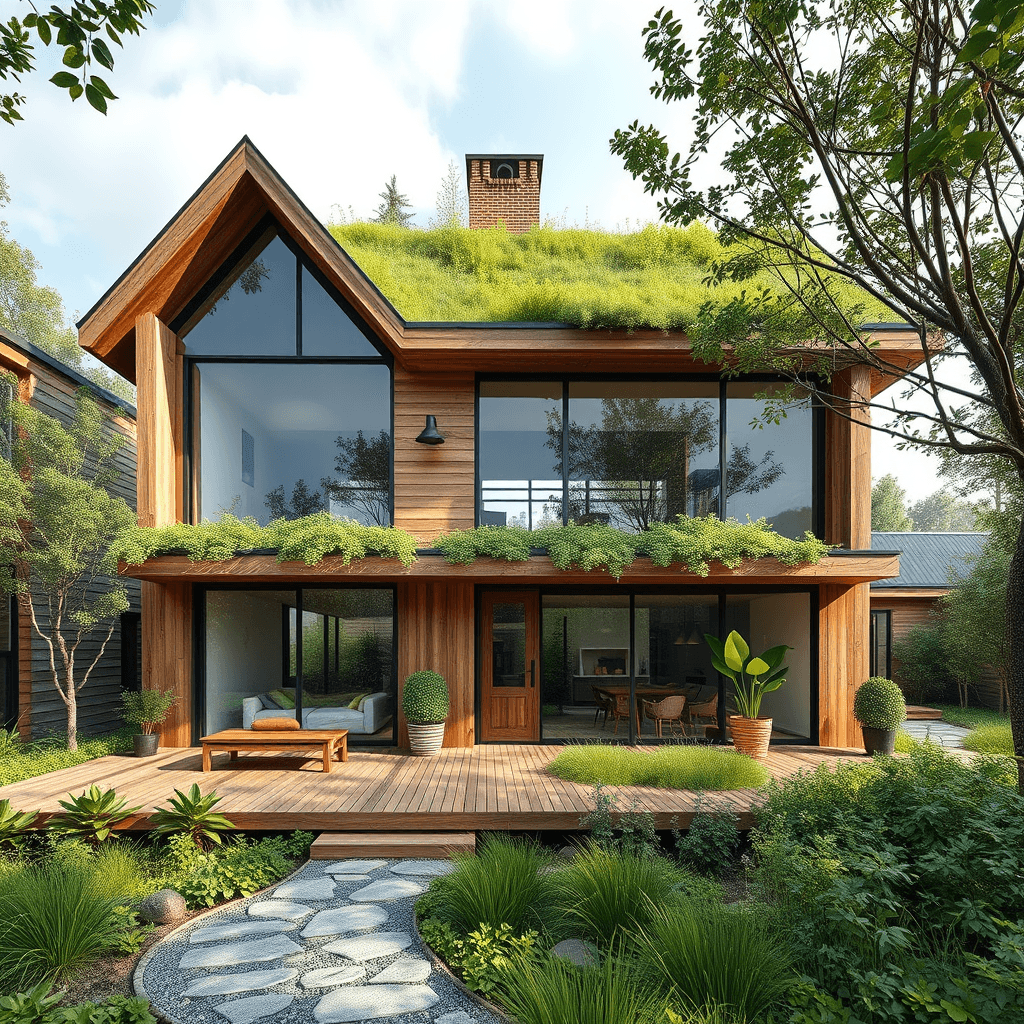
Sustainable architecture is all about designing buildings that minimize environmental impact while maximizing energy efficiency, resource conservation, and occupant well-being. It involves using eco-friendly materials, renewable energy sources, and smart design principles to reduce waste and energy consumption.
Sustainable architecture is not just a trend; it’s a necessity for our planet’s future. As we face the pressing challenges of climate change and resource depletion, the goals of sustainable architecture become increasingly critical. These goals focus on minimizing environmental impact, promoting energy efficiency, and enhancing the well-being of occupants through thoughtful design.
To realize these goals, architects and builders must adopt green sustainable architecture practices that prioritize renewable materials, energy-efficient systems, and innovative design techniques. One effective method is integrating passive solar design principles to maximize natural light and reduce reliance on artificial heating and cooling. Additionally, utilizing recycled or locally sourced materials can significantly diminish the carbon footprint associated with construction.
Moreover, implementing water conservation strategies—such as rainwater harvesting systems or greywater recycling—can lead to significant reductions in water usage. By embracing these practices, we not only contribute to a healthier environment but also create spaces that inspire connection with nature.
**Key Features of Sustainable Architecture:**
1. **Energy Efficiency:**
– Using insulation, energy-efficient windows, and passive solar design to reduce heating/cooling needs.
– Incorporating renewable energy sources like solar panels and wind turbines.
– Implementing smart lighting and HVAC systems to optimize energy use.
2. **Sustainable Materials:**
– Using recycled, reclaimed, or rapidly renewable materials like bamboo, cork, or recycled steel.
– Reducing reliance on concrete (a major CO₂ emitter) by using alternatives like rammed earth or hempcrete.
– Prioritizing locally sourced materials to reduce transportation emissions.
3. **Water Conservation:**
– Installing rainwater harvesting systems.
– Using low-flow fixtures and water-recycling systems.
– Designing landscapes with drought-resistant plants to reduce irrigation needs.
4. **Waste Reduction & Circular Design:**
– Prefabricated and modular construction to minimize material waste.
– Designing buildings for adaptability, so they can be repurposed rather than demolished.
– Recycling and repurposing construction waste.
5. **Healthy Indoor Environment:**
– Maximizing natural ventilation and daylighting to reduce artificial lighting and air conditioning.
– Using non-toxic, low-VOC (volatile organic compounds) paints and materials for better indoor air quality.
Ultimately, sustainable architecture is about creating a harmonious balance between human needs and environmental stewardship. By committing to these goals and methods today, we can build a resilient future that respects our planet while providing functional and beautiful spaces for generations to come.